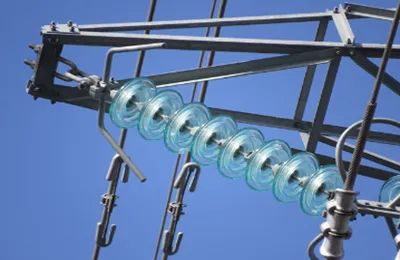
Manufacturing Process of Glass Electrical Insulators
Glass electrical insulators are used in power transmission and distribution systems to support and isolate electrical conductors, ensuring that electrical energy is transmitted efficiently and safely. The manufacturing of these insulators involves several steps to ensure they meet high standards of strength, durability, and electrical resistance. Below is a breakdown of the manufacturing process:
1. Material Selection
Raw Materials: The primary materials used in the manufacturing of glass insulators include silica (sand), soda ash, and limestone. These materials are mixed in specific proportions to form a glass with high dielectric strength.
Additives: Other additives such as alumina and magnesium oxide may be added to enhance the glass's properties, such as increasing strength or resistance to weathering.
2. Batch Mixing
The raw materials are carefully weighed and mixed to ensure the proper chemical composition. The mix is then homogenized to avoid any inconsistency in the final product.
3. Melting
The mixture is fed into a glass furnace where it is heated to temperatures between 1,400°C and 1,600°C (2,550°F to 2,900°F). At these high temperatures, the raw materials melt and form a uniform glass mass.
The molten glass is continuously stirred to eliminate bubbles and achieve uniform viscosity.
4. Forming the Insulator
The molten glass is poured into insulator molds. Depending on the design of the insulator, this can be done through different processes, such as pressing or blowing:
Pressing Process: A pre-determined amount of molten glass is placed into a mold, and a plunger presses the glass into the desired shape.
Blowing Process: Molten glass is placed into a mold and air is blown into it to form the hollow parts of the insulator.
5. Annealing
After shaping, the insulator must undergo annealing. The insulators are slowly cooled in an annealing oven (lehr) to relieve internal stresses created during the rapid cooling of the glass from its molten state.
This process ensures that the glass is durable and resistant to cracking under mechanical or thermal stress.
6. Surface Treatment
The surfaces of the insulators are polished to remove any sharp edges or imperfections that could affect performance. In some cases, a chemical coating may be applied to enhance the glass’s resistance to environmental degradation.
7. Quality Control and Inspection
Insulators are subjected to visual inspection and mechanical testing to detect cracks, bubbles, or any deformities. High voltage electrical testing is also performed to ensure that the insulators can withstand the operating conditions for which they are designed.
Mechanical Testing: Includes tension tests to ensure the insulator can withstand the mechanical loads during installation and operation.
Electrical Testing: This includes flashover tests and puncture voltage tests to check the insulator's electrical performance.
8. Final Finishing and Packaging
Once inspected and tested, the insulators are cleaned and packed for shipping. Special care is taken to ensure they are transported without damage, as even small defects can affect performance in the field.