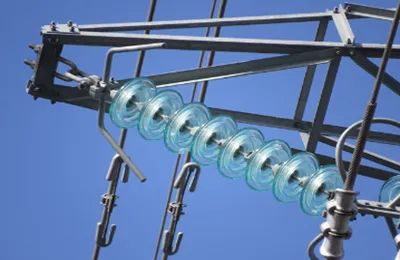
Power suspension disc insulator are disc-shaped due to a combination of electrical, mechanical, and environmental design considerations:

Increased Creepage Distance: The disc shape creates a longer path along the surface (creepage distance), making it harder for electrical current to leak. Multiple discs in a string further extend this path, accommodating higher voltage levels by adding more discs.
Water Shedding: The disc's design allows rainwater to drip off the edges, preventing continuous water films that could conduct electricity. This reduces leakage currents and maintains insulation effectiveness.
Mechanical Strength: Discs distribute mechanical stress evenly, supporting the weight of power lines while withstanding environmental forces like wind. Their shape and arrangement in strings provide flexibility and durability.
Modularity: Discs can be stacked in series, enabling customizable insulation levels for different voltages. This modularity offers cost-effective scalability.
Electric Field Distribution: Rounded edges minimize electric field concentration, reducing the risk of corona discharge and associated energy loss or damage.
Manufacturing and Contamination Resistance: Discs are easier to mold from glass, with smooth surfaces or ridges that resist contamination buildup. This design also aids in shedding dirt and pollutants.
Historical Standardization: Over time, the disc shape proved optimal through experimentation, leading to its widespread adoption in both glass and ceramic insulators.
These factors collectively ensure reliable insulation, structural integrity, and longevity in diverse environmental conditions.
Here are some related Q&As that expand on the topic of power line insulators and their design:
Q1: Why are glass and ceramic commonly used for insulators?
A: Glass and ceramic are non-conductive, weather-resistant, and mechanically robust. They resist surface leakage currents, endure high voltages, and withstand environmental stressors (UV radiation, temperature swings, and pollution). Glass also allows visual inspection for cracks, while ceramic offers superior mechanical strength.
Q2: Why not use a single solid insulator instead of multiple discs?
A: A single solid insulator would require an impractically large size to handle high voltages. Multiple discs in a "string" allow modularity: each disc adds insulation (creepage distance), and the air gaps between them interrupt potential electrical arcs. This design is also lighter and cheaper to manufacture.
Q3: How does voltage relate to the number of discs in a string?
A: Each disc typically handles 10–15 kV, depending on design. For example:
11 kV lines: 1–2 discs.
230 kV lines: 12–15 discs.
Higher voltage lines (e.g., 500 kV) use longer strings (20+ discs) to prevent flashovers.