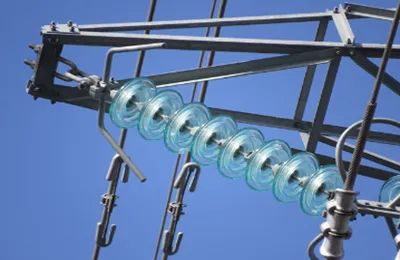
High tension insulators are crucial components in the electrical power transmission system, designed to support and insulate conductors at high voltages. Here’s an overview of the main types of insulators used for high tension applications:
Types of High Tension Insulators
1. Suspension Insulators
Description: These insulators are primarily used for medium to high-voltage transmission lines. They consist of several porcelain discs connected in series by metal links.
Function: They support the conductors and insulate them from supporting structures, effectively increasing the overall flashover voltage when arranged in series.
Voltage Range: Typically used for voltages from 33 kV to several hundred kV.
2. Strain Insulators
Description: Also known as tension insulators, they are designed to absorb the tension in conductors, particularly in areas where lines change direction or at dead ends.
Construction: Made up of porcelain discs connected by metal links, they provide both insulation and mechanical strength.
Application: Commonly used in medium to high-voltage transmission lines.
3.
Post Insulators
Description: These consist of a single solid piece of porcelain or glass mounted on a metal base.
Advantages: They have excellent mechanical strength and high flashover voltage capability.
Usage: Widely utilized in substations and for applications requiring insulation from supporting structures, suitable for voltages from 11 kV to several hundred kV.
4.
Long Rod Insulators
Description: Designed to withstand both mechanical and electrical stresses, these consist of a long porcelain rod providing a continuous current path from the conductor to the tower.
Benefits: They offer superior mechanical strength and pollution performance, making them ideal for extra-high voltage (EHV) and ultra-high voltage (UHV) applications.
5.
Composite Insulators
Description: Also known as polymer or rubber insulators, they are lighter and smaller than traditional glass or porcelain insulators.
Advantages: They resist dust accumulation and have higher mechanical strength, making them suitable for extreme weather conditions.
Limitations: However, they may deteriorate under excessive heat due to overcurrent or faults.
6. Glass Insulators
Description: Made from high-quality tempered glass, these insulators can endure significant mechanical and thermal stresses while withstanding high electrical tension.
Features: They often include additional coatings to enhance hydrophobic properties, improving performance in contaminated environments.
High tension insulators play a vital role in ensuring safe and efficient power transmission. The choice of insulator depends on various factors including voltage level, environmental conditions, and mechanical requirements. Common materials used include porcelain, glass, and composite polymers, each offering unique advantages suited to different applications in the power grid.