High-Tension (HT) lines, which operate at high voltage levels (typically above 1 kV), require insulators that can withstand both high electrical stress and challenging environmental conditions. The types of insulators used in HT lines are designed to provide electrical insulation, mechanical support, and resistance to external factors like weather, pollution, and mechanical loading. Here are the main types of insulators used in HT lines:
1. Porcelain Insulators
Description:
Porcelain insulators are made from ceramic materials and are widely used for medium to high voltage applications. They have a high dielectric strength, are durable, and offer good mechanical strength.
Advantages:
High mechanical strength
Good electrical insulating properties
Resistant to UV and weathering
Applications: Commonly used in HT overhead transmission lines and substation equipment.
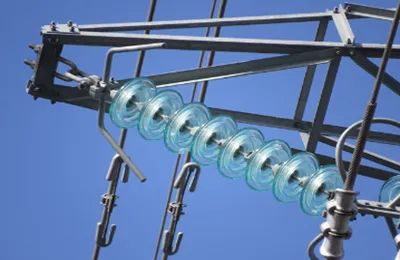
2. Glass Insulators
Description:
Glass insulators are made of toughened glass, which is highly resistant to environmental factors and electrical stress. They are transparent, allowing for easy inspection of their condition.
Advantages:
High resistance to contamination and pollution
Better visibility for inspection
Can withstand high mechanical stresses
Applications: Frequently used in areas with high contamination levels (pollution or salt), or where insulator maintenance and inspection are crucial.
3. Polymer (Composite) Insulators
Description: Polymer insulators are made with a combination of polymeric materials, usually silicone rubber, and a fiberglass core. These insulators have a lighter weight compared to porcelain and glass insulators.
Advantages:
Lightweight and easy to transport and install
High resistance to corrosion and contamination
Lower risk of breakage compared to porcelain and glass
Applications: Increasingly used in HT lines, especially in areas prone to pollution or coastal environments, as they are more resistant to the accumulation of dirt and moisture.
4. Suspension Insulators
Description: Suspension insulators are designed to hang the conductors from the towers and are used for high-voltage transmission lines. These insulators are typically made of porcelain or glass discs connected in series.
Advantages:
Provide mechanical strength to support the weight of the conductors
Suitable for long-distance transmission lines
Applications: Used in HT transmission lines that span long distances, especially for 33 kV and above voltage lines.
5. Pin Insulators
Description: Pin insulators are mounted directly on the supporting structure (typically a metal pin on a utility pole) and are commonly used for medium to high voltage applications. These insulators have a metal base that allows them to be fixed onto the pole or tower.
Advantages:
Simple and economical design
Easy to install and maintain
Applications: Primarily used in overhead HT lines for voltages ranging from 11 kV to 66 kV.