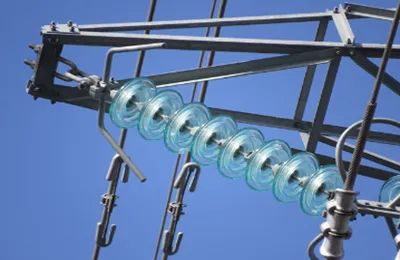
an electrical insulator, at its core, is a material that inhibits the movement of electric charge. unlike conductors, which facilitate the flow of electrons, insulators act as barriers, preventing the unintended transmission of electric current. the fundamental property that distinguishes insulators is their high resistivity. resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. insulators exhibit a high resistivity, effectively impeding the movement of electrons.
common materials used as electrical insulators include rubber, glass, porcelain, plastic, and certain types of ceramics. these substances possess the necessary characteristics to resist the flow of electricity and are strategically employed in various electrical applications.
properties of electrical insulators:
understanding the properties of electrical insulators is essential to grasp their functionality in electrical systems. one primary property is resistivity, measured in ohm-meters (ω·m). high resistivity is a defining feature of insulators, and it ensures that these materials offer significant opposition to the flow of electric current. this property is crucial for maintaining separation between conductive elements in electrical circuits.
another essential property is dielectric strength, which measures the maximum electric field a material can endure without experiencing electrical breakdown. dielectric strength is vital in applications where insulators are subjected to high voltages. materials with high dielectric strength are preferred in such scenarios to prevent unintended electrical discharges.
thermal stability is also a key consideration. electrical insulators must withstand a range of temperatures without compromising their insulating properties. this is particularly important in electrical systems where heat is generated, ensuring that the insulating materials remain effective under varying thermal conditions.
applications of electrical insulators: electrical insulators find wide-ranging applications in diverse areas, contributing to the functionality and safety of electrical systems.
wiring insulation: one of the most common applications of electrical insulators is in the insulation of electrical wires. the outer covering of wires is typically made of insulating materials to prevent unintended contact with conductive materials, reducing the risk of electric shocks and short circuits.
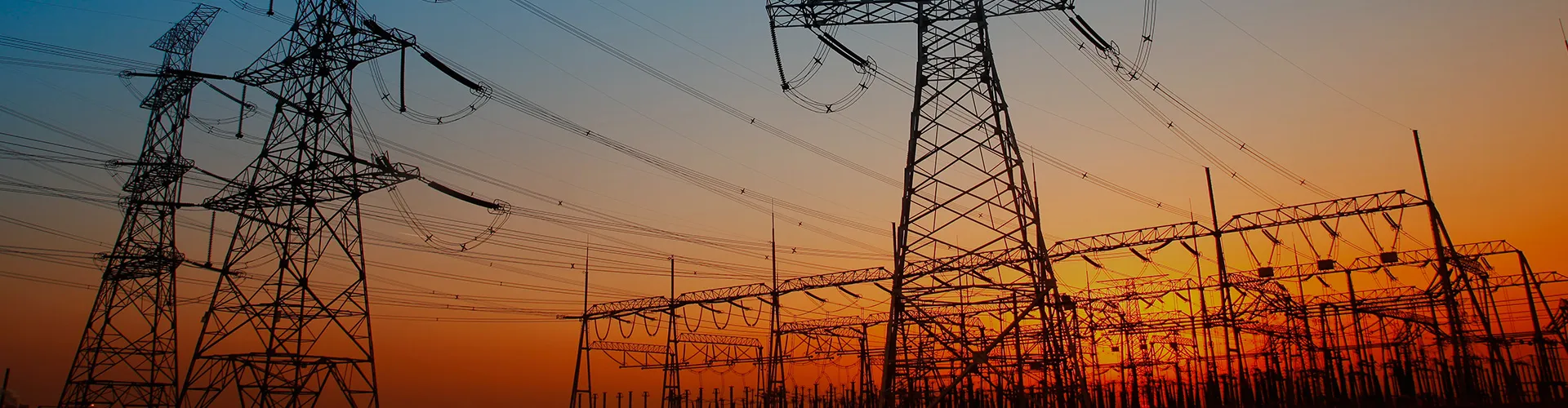
support for electrical components: electrical insulators are used as supports for various components in electrical systems. for example, insulating materials are employed in the construction of electric poles and towers, preventing the unwanted flow of current to the ground.
transformer insulation: transformers, crucial components in power distribution systems, utilize insulating materials to separate different windings and prevent electrical leakage. the insulators in transformers contribute to the overall efficiency and safety of power transmission.
capacitors and insulating layers: in electronic devices, capacitors store electrical energy. insulating layers in capacitors prevent the flow of current between the capacitor plates, enabling the device to store and release electrical energy as needed.
power line insulation: overhead power lines, which transport electricity over long distances, rely on insulators to support the conductors and prevent the loss of electrical energy to the surroundings. insulators in power lines also play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of the lines.
significance of electrical insulators:
the use of electrical insulators holds immense significance in the realm of electrical engineering and power distribution for several reasons.
safety: perhaps the foremost importance of electrical insulators is their role in ensuring safety. by preventing the unintended flow of electric current, insulators minimize the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage.
efficiency: insulators contribute to the efficiency of electrical systems by containing and directing the flow of current along desired paths. this controlled flow reduces energy losses and ensures that electrical power is transmitted and utilized efficiently.
reliability: electrical insulators enhance the reliability of electrical infrastructure. they prevent short circuits and other electrical faults, minimizing the chances of disruptions in power supply and ensuring the smooth operation of electrical systems.
equipment protection: insulating materials safeguard electrical equipment from damage caused by environmental factors and electrical disturbances. they provide a protective barrier that shields sensitive components from adverse conditions, extending the lifespan of electrical devices and systems.
electrical insulators play a critical role in the intricate web of electrical systems that power our modern world. from the wiring in our homes to the vast networks of power distribution, these materials provide the necessary isolation and protection to ensure the safe and efficient utilization of electricity. as technology continues to advance, the development of new insulating materials and innovative applications will likely further enhance the performance and sustainability of electrical systems.