working principles
the primary function of a composite insulator is to prevent the flow of electrical current between conductive parts while physically supporting the electrical equipment. to understand how composite insulators achieve this, we must consider the working principles involved:
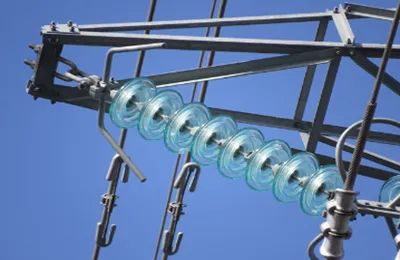
electrical insulation: composite insulators effectively isolate the live conductor from the supporting structure or ground. the silicone rubber housing provides excellent electrical insulation properties, ensuring that current does not flow through the insulator and cause electrical faults or flashovers.
mechanical support: the core rod, made from fiberglass or epoxy resin, imparts mechanical strength to the insulator. it allows the insulator to support the weight of electrical conductors and other components while resisting mechanical stresses such as wind, ice, and vibrations.
resistance to environmental factors: silicone rubber is highly resistant to environmental factors that can degrade traditional ceramic insulators, such as moisture, uv radiation, and pollution. this resistance ensures the long-term reliability and performance of composite insulators in harsh outdoor conditions.
advantages of composite insulators
composite insulators offer several significant advantages over their ceramic counterparts, making them a preferred choice in many applications:
lightweight: composite insulators are significantly lighter than ceramic insulators, making them easier to transport, install, and handle.
excellent pollution performance: they are highly resistant to pollution and contamination, reducing the risk of flashovers in polluted environments.
long service life: composite insulators have a longer service life than ceramic insulators due to their superior resistance to environmental factors and aging.
reduced maintenance: their durability and reliability reduce the need for frequent maintenance and inspection.
high mechanical strength: composite insulators can withstand mechanical stresses, such as wind and ice loads, without compromising their electrical performance.
customizable: they can be designed and manufactured in various shapes and sizes to suit specific applications.
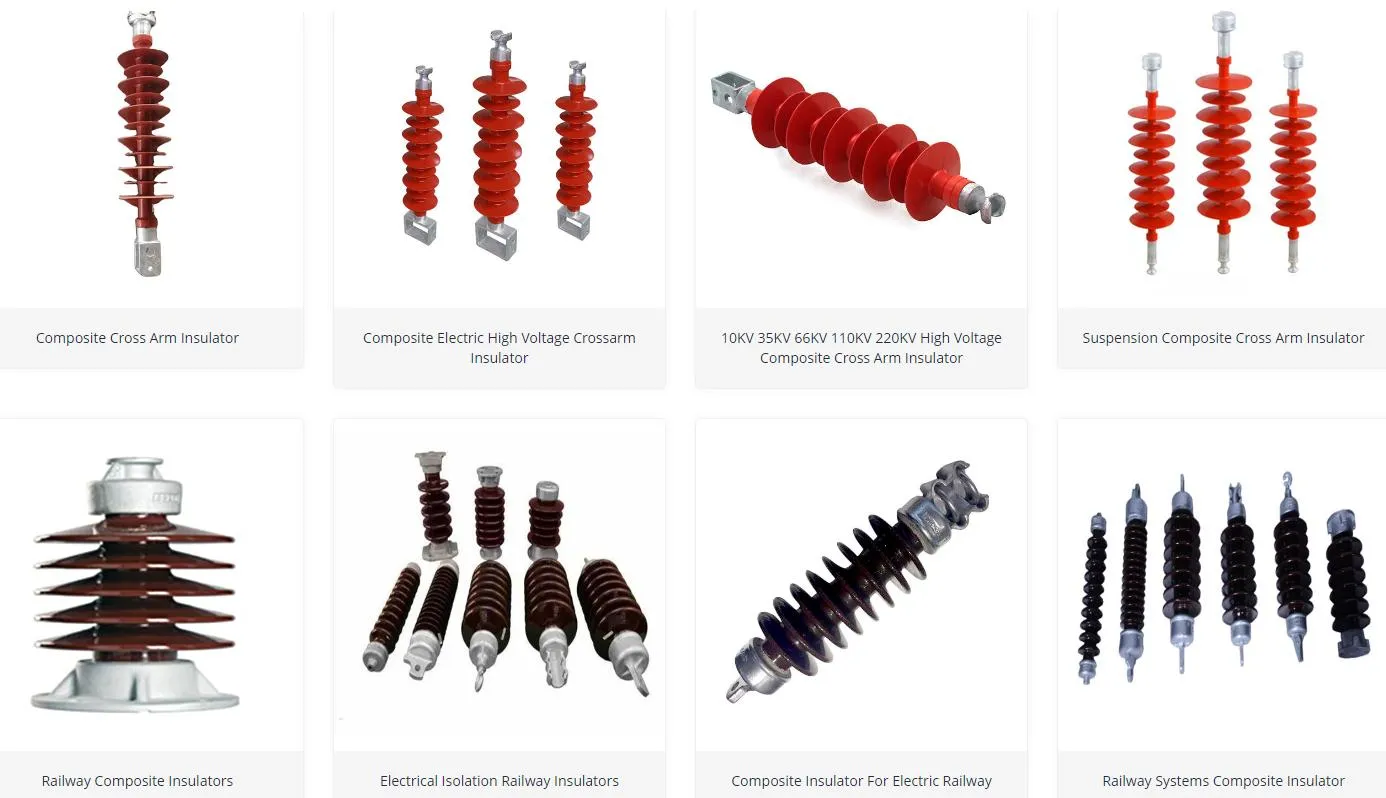
applications
composite insulators find extensive use in a wide range of applications within the electrical and power transmission industry:
high-voltage transmission lines: they are commonly used for insulating high-voltage transmission lines, where their lightweight design and pollution resistance are advantageous.
substations: composite insulators are used in substations to support and insulate various electrical equipment, including circuit breakers, transformers, and switches.
railway electrification: they play a crucial role in electrified railway systems, where they insulate overhead wires and support the catenary system.
wind and solar farms: these insulators are suitable for renewable energy installations, as they can withstand the environmental challenges posed by remote locations.
industrial facilities: composite insulators are employed in various industrial settings to insulate electrical equipment and ensure safe and reliable operations.
urban distribution networks: they are used in urban distribution networks to insulate power lines and reduce the visual impact of overhead lines on the urban landscape.
in conclusion, composite insulators represent a remarkable evolution in electrical insulation technology. their unique composition, working principles, and numerous advantages have made them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications in the electrical and power transmission industry. with their exceptional durability and performance, composite insulators continue to play a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and reliable distribution of electrical energy across the globe.