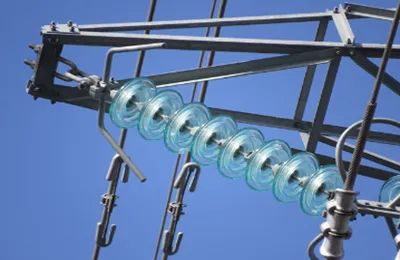
rod post insulators and line post insulators are both essential components in electrical power systems, particularly in high-voltage transmission and distribution lines. they serve the common purpose of providing electrical insulation and mechanical support to conductors, but they differ in their designs and applications. here are the key differences between rod post insulators and line post insulators:
1. design and structure:
rod post insulators: rod post insulators are typically made of a single, solid cylindrical or conical insulating rod, often composed of materials like porcelain, glass, or composite materials. they have one or more sheds or skirts (extensions) arranged along the length of the rod. the sheds are designed to provide additional surface creepage distance, which enhances the insulator's performance in polluted or wet environments. the top and bottom ends of the rod typically have metal fittings for attaching to the supporting structure and the conductor, respectively.
line post insulators: line post insulators consist of multiple insulating units stacked or assembled in series, forming a long column-like structure. these insulating units are typically made of porcelain or composite materials. line post insulators are often designed with additional grooves and sheds to increase their leakage path and provide better pollution performance. they also have metal end fittings for attachment to the supporting structure and conductors.
2. application:
rod post insulators: rod post insulators are commonly used in distribution systems, substation equipment, and medium-voltage applications. they are suitable for supporting both horizontal and vertical conductors and are often used where space is limited.
line post insulators: line post insulators are primarily used in high-voltage transmission lines, substations, and overhead distribution systems. they are designed for the specific requirements of these high-voltage applications and are often used to support conductors in a horizontal or sloping configuration.
3. voltage rating:
rod post insulators: rod post insulators are typically used in applications with lower voltage ratings, such as medium voltage (typically up to 36 kv) systems.
line post insulators: line post insulators are designed for high-voltage applications and can be used in transmission lines with voltage ratings ranging from 69 kv and above.
4. pollution performance:
rod post insulators: while rod post insulators are suitable for many applications, they may not provide the same pollution performance as line post insulators due to their simpler design. they are generally used in less polluted environments.
line post insulators: line post insulators are designed with features such as sheds, grooves, and longer leakage paths to enhance their resistance to pollution, making them suitable for use in areas with a higher risk of contamination, such as coastal regions or industrial areas.
5. mechanical load handling:
rod post insulators: rod post insulators are designed to handle both mechanical loads (tension and compression) and electrical loads. they are often used in applications where mechanical stresses are moderate.
line post insulators: line post insulators are specifically engineered to handle high mechanical loads, including tension, compression, and bending forces, in addition to their electrical insulation function. this makes them suitable for use in long-span transmission lines and other high-stress environments.
all in all, rod post insulators are typically used in lower voltage and less demanding applications, while line post insulators are designed for high-voltage transmission systems and applications with higher mechanical and pollution challenges. the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the electrical power system and the environmental conditions in which they will be used.