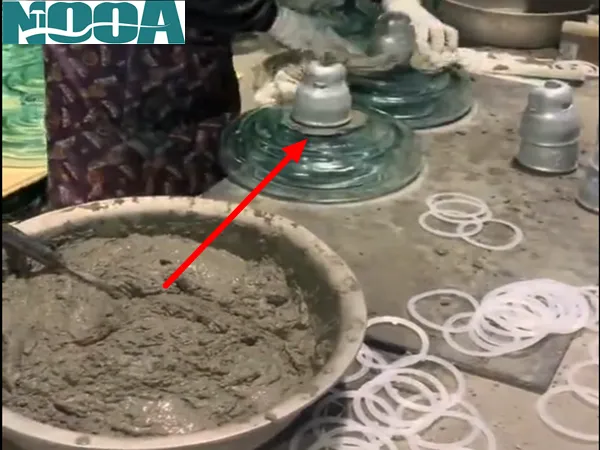
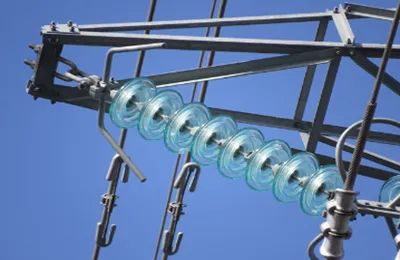
Common Types of Cementing Agents and Their Comparative Advantages
Rapid-Hardening Portland Cement Agent
The outstanding feature of rapid-hardening Portland cement is its fast early strength development. Compared to ordinary Portland cement, rapid-hardening Portland cement can achieve higher strength more quickly at the same early age. Relevant data indicate that the compressive strength growth of rapid-hardening Portland cement at 1-3 days is significantly higher than that of ordinary Portland cement, with the 3-day compressive strength reaching a high value. This characteristic is of great importance in the insulator production process, as it significantly shortens the production cycle and improves efficiency. For urgent projects or those with high demands on production schedules, rapid-hardening Portland cement can meet the needs for rapid production and installation, allowing insulators to be put into use more quickly and reducing project waiting times.
Sulphoaluminate Cement Agent
Sulphoaluminate cement demonstrates significant advantages in the field of high-voltage glass power insulators due to its unique properties. It features early strength and high strength, with an extremely fast rate of early strength development. Research shows that sulphoaluminate cement can achieve high compressive and flexural strength within 1-2 days, with the 1-day compressive strength reaching a high level, quickly meeting the insulator's strength requirements for the cement. Furthermore, sulphoaluminate cement possesses good impermeability and frost resistance. In harsh environments that are humid and cold, ordinary cement may suffer from performance degradation or even structural damage due to water penetration and freeze-thaw cycles. However, with its dense microstructure, sulphoaluminate cement can effectively resist water penetration and reduce damage caused by freeze-thaw cycles, providing a strong guarantee for the long-term stable operation of insulators in harsh environments.
Composite Cement Agent
A composite cement agent is a type of cement made by combining multiple types of cement or adding special admixtures. It can integrate the advantages of multiple cements and compensate for the performance deficiencies of a single cement agent. By rationally proportioning different components, the performance of the cement can be optimized according to actual usage needs. For example, by compounding Portland cement with sulphoaluminate cement and adding an appropriate amount of admixtures like silica fume, the resulting composite cement has both the long-term strength stability of Portland cement and the early high-strength characteristics of sulphoaluminate cement. At the same time, the silica fume can fill the pores of the cement stone, increasing the density of the cementing agent and thereby enhancing its durability and impermeability. This type of composite cement can better adapt to the complex and variable high-voltage power environment, providing more comprehensive and reliable performance support for glass insulators.
High-Alumina Cement Agent
High-alumina cement is a hydraulic cementing material made from bauxite and limestone as primary raw materials, which are calcined and finely ground. In the application of high-voltage glass power insulators, high-alumina cement has unique advantages. In terms of strength performance, high-alumina cement exhibits extremely rapid early strength growth; its 1-day compressive strength can reach a high value, sometimes even comparable to sulphoaluminate cement, and its later-stage strength is stable without retrogression, providing durable and reliable bonding strength for the insulator. High-alumina cement has excellent high-temperature resistance, maintaining good mechanical properties in high-temperature environments. When a high-voltage power system experiences localized high temperatures due to faults or other reasons, ordinary cement may lose strength and suffer structural damage. However, high-alumina cement, with its high-temperature resistance, can maintain the structural stability of the insulator, safeguarding the power system's security. Additionally, high-alumina cement has strong resistance to sulfate attack. In areas where the soil or environment has a high sulfate content, it can effectively resist sulfate corrosion of the cement, extending the service life of the insulator. Compared to some other cements, it shows outstanding performance in terms of durability.
In the selection process of cementing agents for high-voltage glass power insulators, it is necessary to strictly adhere to relevant standards and fully consider the characteristics and advantages of different types of cementing agents. Rapid-hardening Portland cement can shorten production cycles, sulphoaluminate cement performs excellently in harsh environments, composite cement allows for performance customization, and high-alumina cement has significant advantages in high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. By comprehensively balancing factors such as actual engineering needs, cost budgets, and environmental conditions, selecting the most suitable cementing agent is the only way to ensure that high-voltage glass power insulators have excellent performance, are safe and reliable, and lay a solid foundation for the stable operation of the high-voltage power system.