Why Disc-Shaped Insulators Are Better Than Solid Insulators in High-Voltage Power Systems
Disc-shaped insulators, also known as cap-and-pin insulators, are widely used in high-voltage and extra-high-voltage transmission lines, while solid insulators are more common in low- and medium-voltage applications. The modular design, superior mechanical flexibility, easier maintenance, and better electrical performance under harsh conditions make disc-shaped insulators a preferred choice for modern power grids. Let's learn together with
Nooa Electric in detail why disc-shaped insulators outperform solid insulators, covering mechanical, electrical, operational, and economic perspectives.
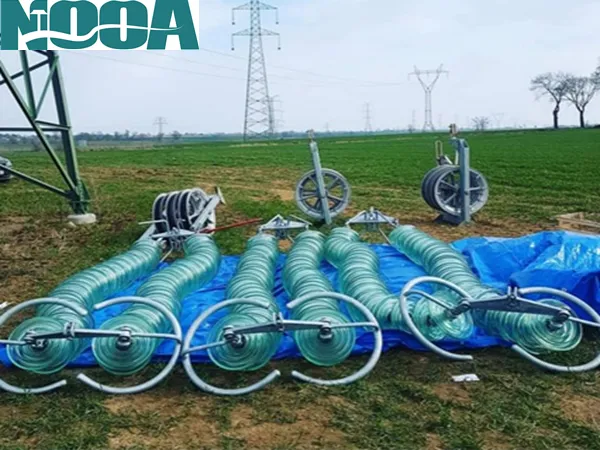

Structural Differences Between Disc-Shaped and Solid Insulators
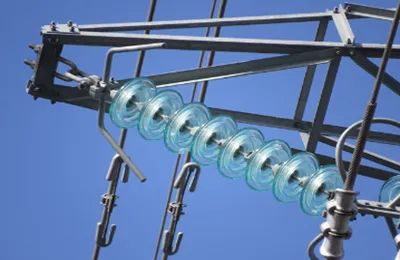
Disc-shaped insulators use a modular cap-and-pin design, while solid insulators are single-piece structures.
Disc-shaped insulators consist of individual units connected in series to form an insulator string. Each unit includes a metal cap, a pin, and an insulating body made of toughened glass, porcelain, or composite materials.
Solid insulators, by contrast, are manufactured as one continuous piece with fixed dimensions. While simple in structure, they lack flexibility in adapting to different voltage levels and mechanical requirements.
Flexibility in Voltage Rating and Insulation Design
Disc-shaped insulators allow flexible voltage configuration by adjusting the number of discs.
One of the greatest advantages of disc-shaped insulators is their scalability. Engineers can increase or decrease the number of discs in a string to meet specific voltage requirements without redesigning the entire structure.
Solid insulators have fixed insulation length and creepage distance, meaning different voltage levels require entirely different insulator designs. This limits their adaptability in transmission systems.
Nooa Electric leverages this modular approach to supply insulator strings optimized for various voltage classes and pollution levels.
Superior Performance Under Mechanical Stress
Disc-shaped insulators distribute mechanical loads more evenly and safely.
In overhead transmission lines, insulators must withstand conductor tension, wind load, ice load, and dynamic vibration. Disc-shaped insulator strings distribute these forces across multiple units, reducing stress concentration.
If one disc experiences damage, the remaining units continue to support the mechanical load, maintaining line integrity. Solid insulators, however, may fail entirely if structural damage occurs at a critical point.
Easier Detection of Defects and Damage
Disc-shaped insulators are easier to inspect and diagnose in service.
Toughened glass disc insulators have a unique advantage: when damaged, they shatter visibly while retaining residual mechanical strength. This makes defect identification during line patrols straightforward.
Solid insulators, especially porcelain types, may develop internal cracks that are difficult to detect visually, increasing the risk of sudden failure.
This clear fault visibility is a major reason many utilities continue to favor disc-shaped glass insulators supplied by manufacturers like Nooa Electric.
Improved Maintenance and Replacement Efficiency
Individual disc units can be replaced without dismantling the entire string.
Maintenance efficiency is another key advantage. If a single disc-shaped insulator fails, only that unit needs to be replaced. This reduces outage time, labor costs, and operational risk.
With solid insulators, damage often requires full replacement, leading to higher maintenance costs and longer service interruptions.
Better Performance in Polluted and Harsh Environments
Disc-shaped insulators perform better in polluted environments due to optimized profiles and creepage design.
Disc-shaped insulators can be designed with:
These features significantly improve resistance to pollution flashover. Solid insulators, due to geometric limitations, are less flexible in achieving long creepage distances without becoming excessively large.
Higher Reliability and System Redundancy
Disc-shaped insulators provide built-in redundancy for transmission safety.
Because insulator strings consist of multiple units, the system does not rely on a single insulating body. This redundancy enhances overall reliability and reduces the risk of catastrophic line failure.
Solid insulators lack this redundancy, making them less suitable for high-voltage and critical transmission corridors.
Economic Advantages Over the Life Cycle
Disc-shaped insulators offer lower life-cycle costs despite higher initial complexity.
Although disc-shaped insulators may involve more components, their:
-
Long service life
-
Easy maintenance
-
Reduced outage risk
-
Adaptability to upgrades
often result in lower total cost of ownership. Utilities working with Nooa Electric benefit from standardized disc designs that simplify inventory and long-term asset management.
Typical Applications Where Disc-Shaped Insulators Excel
Disc-shaped insulators are ideal for high-voltage and extra-high-voltage transmission lines.
They are commonly used in:
-
66kV to 1000kV overhead transmission lines
-
Suspension and tension insulator strings
-
Long-span river crossings
-
High-wind and heavy-ice regions
-
Polluted industrial and coastal zones
Solid insulators are generally limited to distribution lines, substations, or low-voltage applications.
FAQ: Disc-Shaped Insulators vs. Solid Insulators
Q1: Are disc-shaped insulators stronger than solid insulators?
A: Yes, especially in mechanical load distribution and redundancy.
Q2: Why are disc-shaped insulators preferred for high voltage?
A: Their modular design allows flexible voltage ratings and better electrical performance.
Q3: Do disc-shaped insulators require more maintenance?
A: No. In practice, they reduce maintenance time because only damaged discs need replacement.
Q4: Are solid insulators ever better?
A: Solid insulators are suitable for compact, low-voltage, or space-limited installations.
Q5: Can disc-shaped insulators be used in polluted areas?
A: Yes, especially with long creepage designs or RTV coatings.