Company
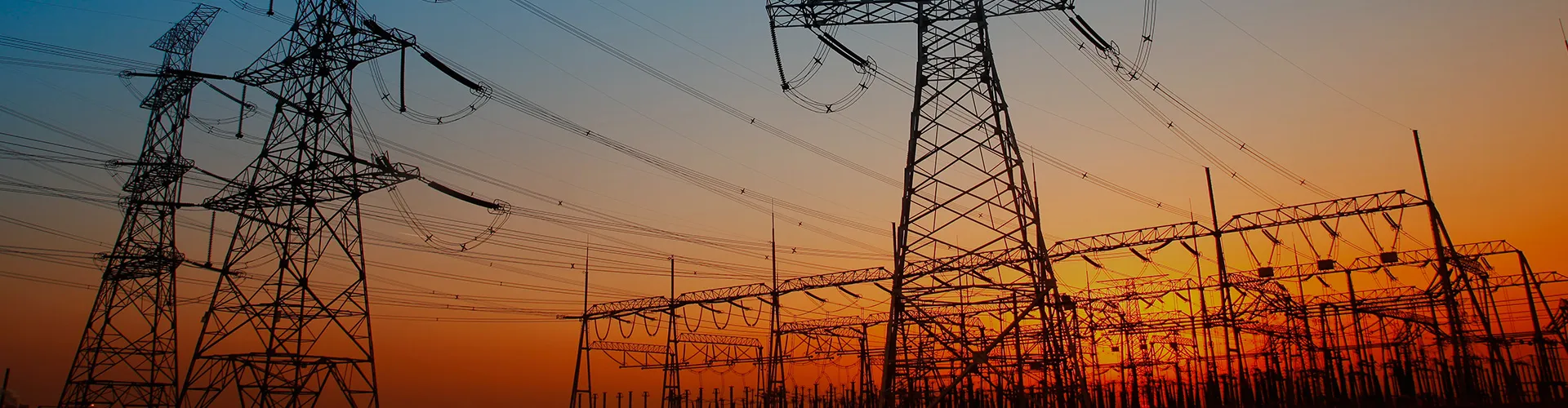
nooa electric co.,ltd. covering an area of 70,000 square meters, and construction area is 50,000 square meters since its establishment in december, 2002. there are more than 200 employees, including 25 technicians. The production Capacity 3500000 pieces per year, and now setting up the new kiln and lines up to 10500000 pieces per year

-
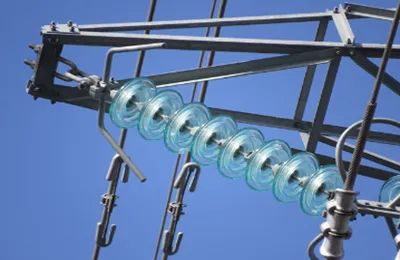
Glass Insulator
Standard Glass Electrical Insulator
Fog Type Glass Insulator
Anti Pollution Toughened Glass Insulator
Open Air Type Glass Powerline Insulator
OUTERIB Glass Power Line Insulators
D.C Glass Disc Insulator
Ground Wire Glass Insulators
RTV Glass Insulators
-
Porcelain Insulator
Porcelain Disc Insulator
Line Post Insulators
Porcelain Hollow Insulators
Rod Post Insulators
-
Composite Insulator
Composite Post Cross Arm Insulator
Railway Composite Insulator
Line Post Composite Insulator
-
Other Powerline Insulators
Ultra High Voltage insulators
High Voltage insulators
Transmission Line Insulator
Substation Insulators
IEC Standard Insulators
ANSI Standard Insulators
120KN Insulator
160KN Insulator
70KN Insulator
40KN Insulator
550KN Insulator
210KN Insulator
-
Transmission Line Hardware Fittings
Insulator Hardware Fittings
Substation Hardware Fittings
Projects
News