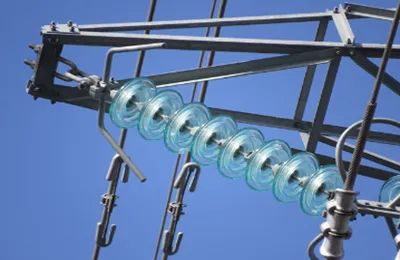
High voltage glass insulators are manufactured using materials selected for their insulating properties, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental factors. The main materials used in the production of high voltage glass insulators are:
1. Toughened (Tempered) Glass
Material Composition: The primary material used in high voltage glass insulators is toughened or tempered glass. This glass is specially formulated to have a high silica content and is typically composed of silica (SiO₂), soda (Na₂O), lime (CaO), and small amounts of other oxides. The composition ensures good dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and resistance to thermal shock.
Properties:
High Mechanical Strength: The tempering process enhances the mechanical strength of the glass, making it resistant to impact and mechanical stress.
Dielectric Properties: Toughened glass has excellent insulating capabilities, which are crucial for withstanding high voltage levels.
Shatter Resistance: When damaged, toughened glass breaks into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of catastrophic failure and minimizing potential damage.
2. Metal Fittings (Cap and Pin)
Material Composition: Metal fittings are usually made from malleable cast iron, forged steel, or galvanized steel for the cap, and steel or forged iron for the pin. These materials are selected for their strength and ability to withstand mechanical loads.
Galvanization: The metal fittings are often hot-dip galvanized to provide a protective zinc coating, which helps prevent corrosion and extends the lifespan of the insulator.
Bonding to Glass: The metal fittings are cemented to the glass using a special adhesive, usually Portland cement or a sulfur cement, to ensure a strong and durable bond.
3. Cement or Adhesive Material
Portland Cement: In traditional glass insulators, Portland cement is used to bond the metal fittings (cap and pin) to the glass body. It ensures a secure mechanical connection and distributes mechanical stresses evenly.
Sulfur Cement: This alternative bonding material is sometimes used due to its rapid setting time and good bonding properties.
4. Additional Considerations:
Coatings: In some cases, an anti-pollution or hydrophobic coating may be applied to the surface of the glass to enhance its resistance to contamination and reduce the risk of flashovers.
Design Variations: Different types of glass insulators may incorporate specific design features, such as increased thickness or specialized shapes, to improve their performance in particular environments or applications.
The combination of toughened glass, metal fittings, and bonding materials results in a robust, high-performance insulator that can withstand the electrical, mechanical, and environmental demands of high voltage power transmission and distribution.
Click to Watch the Glass Insulators Production Process ^.^