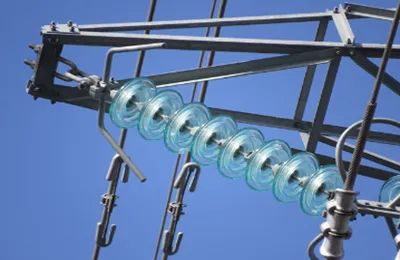
porcelain insulators and
composite insulators are both types of insulating materials used in electrical systems to support and isolate conductors from the supporting structures. however, they differ in terms of their composition, properties, and applications.
here are the key differences between porcelain and composite insulators:
material composition:
porcelain insulators:
these insulators are made of traditional ceramic materials, such as clay, feldspar, and alumina. porcelain insulators are typically glazed to provide a smooth and non-porous surface, making them resistant to moisture and contaminants.
composite insulators:
these insulators are made of a composite material, usually consisting of a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin core. the core is housed in a weather-resistant silicone rubber housing. the use of composite materials allows for greater flexibility in design and improved mechanical and electrical properties.
weight and mechanical strength:
porcelain insulators: porcelain insulators are generally heavier and more brittle compared to composite insulators. they have lower mechanical strength and are more susceptible to breakage under mechanical stress.
composite insulators: composite insulators are lightweight and exhibit higher mechanical strength. the composite materials used provide better resistance to impact and vibration, reducing the risk of breakage during transportation, installation, and operation.
flexibility and design:
porcelain insulators: porcelain insulators are rigid and have limited design flexibility. they are typically produced in standard shapes and sizes.
composite insulators:
the composite material allows for more flexible designs, enabling manufacturers to produce insulators with a variety of shapes and sizes. this flexibility is advantageous in applications where specific design requirements must be met.
electrical performance:
porcelain insulators:
porcelain insulators have good electrical properties and are effective insulators. they provide adequate electrical insulation for various voltage levels.
composite insulators:
composite insulators also offer excellent electrical insulation properties. the combination of the fiberglass core and silicone rubber housing provides good dielectric strength.
corrosion resistance:
porcelain insulators:
porcelain insulators are resistant to chemical corrosion but may develop surface cracks over time, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
composite insulators:
composite insulators are highly resistant to corrosion and offer better performance in polluted or corrosive environments. the silicone rubber housing provides additional protection against environmental factors.
cost:
porcelain insulators:
porcelain insulators are often more cost-effective compared to composite insulators.
composite insulators:
composite insulators may have a higher initial cost, but their advantages in terms of weight, mechanical strength, and flexibility can offset the higher upfront expense.
the choice between porcelain and composite insulators depends on the specific requirements of the electrical system, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.