The Ultimate Guide to Electric Glass Insulators: Everything You Need to Know
In the world of electrical infrastructure, electric glass insulators are essential components that ensure the safety and efficiency of power transmission. These devices, while often overlooked, play a critical role in maintaining the reliability of electrical grids. Now, we'll explore everything you need to know about electric glass insulators, including their types, applications, and benefits. Whether you're a professional in the industry or simply curious, this comprehensive overview will provide you with valuable insights into this vital technology.
What Are Electric Glass Insulators?
Electric glass insulators are specialized devices used in electrical systems to prevent the unwanted flow of electricity from power lines to surrounding structures. Made from high-quality glass, these insulators are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and pollution. The primary function of an electric glass insulator is to support and separate electrical conductors while preventing current from passing through them to the ground.
Types of Electric Glass Insulators
There are several types of electric glass insulators, each designed for specific applications within the electrical grid. Understanding these types can help in selecting the right insulator for various needs:
Pin Type Insulators: These are commonly used in lower voltage applications. Pin type insulators are mounted on a pin on top of a pole and are typically used for distribution lines.
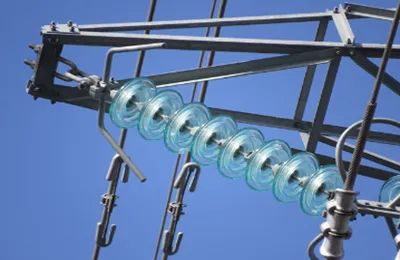
Suspension Insulators: Used for high-voltage transmission lines, suspension insulators consist of a series of glass disks connected in series. These insulators are hung from towers and provide flexibility and strength in supporting heavy power lines.
Strain Insulators: Strain insulators are used to handle mechanical stress in power lines, particularly at sharp turns or where there is a change in direction. They are designed to bear the mechanical load of the line.
Shackle Insulators: These are used in low-voltage applications and are typically mounted on the cross-arm of poles. Shackle insulators are compact and can handle both electrical and mechanical loads.
Type
|
Application
|
Voltage Range
|
Pin Type Insulators
|
Distribution lines
|
Low to Medium
|
Suspension Insulators
|
High-voltage transmission
|
High
|
Strain Insulators
|
Line tension points
|
Medium to High
|
Shackle Insulators
|
Low-voltage applications
|
Low
|
Applications of Electric Glass Insulators
Electric glass insulators are widely used in various sectors, including power generation, transmission, and distribution. Their ability to withstand electrical and environmental stress makes them ideal for a range of applications:
Power Transmission Lines
In high-voltage transmission systems, electric glass insulators are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the power lines. They prevent electricity from leaking into the ground or surrounding structures, ensuring that power is efficiently transmitted over long distances. The use of suspension insulators, in particular, allows for flexibility in line design and reduces the risk of power outages.
Substations
Substations are critical nodes in the electrical grid where voltage levels are adjusted for distribution. Electric glass insulators are used in substations to isolate various components, such as transformers and circuit breakers, from the ground and from each other. This isolation is essential for preventing short circuits and ensuring the safe operation of the substation.
Railways and Electrified Transportation
Electric glass insulators are also used in railway electrification systems, where they support and insulate the overhead wires that supply power to trains. These insulators must be highly durable to withstand the mechanical stress and environmental exposure common in railway systems.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, electric glass insulators are used to isolate machinery and electrical equipment from the ground. This isolation is crucial for protecting both the equipment and the operators from electrical hazards. Industries such as mining, oil and gas, and manufacturing rely on these insulators to maintain safety and operational efficiency.
Advantages of Using Electric Glass Insulators
Electric glass insulators offer several advantages over other types of insulators, such as those made from porcelain or composite materials. These benefits include:
Durability and Longevity
One of the most significant advantages of electric glass insulators is their durability. Glass is resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and pollution, which can degrade other materials over time. As a result, glass insulators have a long service life and require less maintenance.
Superior Electrical Performance
Glass has excellent electrical insulating properties, making it an ideal material for high-voltage applications. Electric glass insulators offer high dielectric strength, meaning they can withstand significant electrical stress without breaking down. This property is particularly important in high-voltage transmission lines, where reliable insulation is critical.
Aesthetic Appeal
Unlike other materials, glass insulators have a clear, translucent appearance that blends well with the environment. This aesthetic quality is particularly valued in urban and suburban areas where the visual impact of infrastructure is a concern.
Resistance to Contamination
Glass surfaces are smooth and non-porous, making them less prone to contamination by dirt, dust, and other pollutants. This resistance to contamination helps maintain the insulator's performance over time, even in harsh environmental conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Electric Glass Insulators
1. What is the primary purpose of an electric glass insulator?
The primary purpose of an electric glass insulator is to support and separate electrical conductors while preventing the unwanted flow of electricity to the ground or surrounding structures.
2. How are electric glass insulators made?
Electric glass insulators are made by heating raw glass materials until they become molten, then molding them into the desired shape. The insulators are then cooled and annealed to improve their strength and durability.
3. What are the advantages of glass insulators over porcelain insulators?
Glass insulators offer superior durability, electrical performance, and resistance to environmental factors compared to porcelain insulators. They also have a longer service life and require less maintenance.
4. Can electric glass insulators be recycled?
Yes, electric glass insulators can be recycled. The glass material can be melted down and reused to produce new insulators or other glass products.
5. How do you maintain electric glass insulators?
Maintaining electric glass insulators involves regular inspections to check for damage or contamination. Cleaning may be necessary in environments with high levels of pollution or dust.
6. Are electric glass insulators still used today?
Yes, electric glass insulators are still widely used in various electrical systems, particularly in high-voltage transmission and distribution networks.
Electric glass insulators are a crucial component in modern electrical systems, providing reliable insulation and support for power lines and equipment. Their durability, superior electrical performance, and resistance to environmental factors make them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from power transmission lines to industrial machinery. If you are interested in our
NOOA Glass Insulators pls send your inquiry to:
info@nooaelectric.com