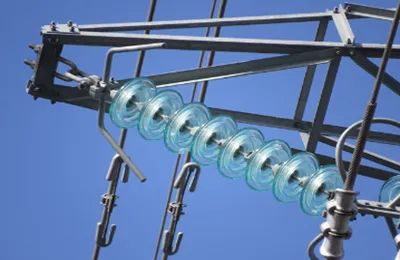
Detailed Overview of the 3 Types of Suspension Insulator Caps
Suspension insulator caps are critical components in overhead power transmission systems, ensuring reliable mechanical and electrical connections between conductors and towers. The three main types of suspension insulator caps—Clevis, Socket, and Tongue—each have unique designs and applications, tailored to specific mechanical and electrical demands.
1. Clevis Type Suspension Insulator Caps
Design & Features:
The clevis type has a U-shaped configuration, resembling a fork, with two parallel arms and a pinhole for securing the insulator.
It works in conjunction with a clevis pin and a cotter pin to ensure a strong mechanical connection.
Often made of hot-dip galvanized steel or aluminum alloy, these caps provide excellent resistance to corrosion and mechanical stress.
Applications:
Used in medium to high-voltage lines where ease of assembly and disassembly is important.
Ideal for situations requiring alignment adjustments, as the clevis design allows for minor positional flexibility.
Advantages:
Strong and durable under heavy mechanical loads.
Easy to assemble and maintain.
2. Socket Type Suspension Insulator Caps
Design & Features:
The socket type cap is a closed, cup-shaped component that encloses the ball head of the mating fitting.
The connection is secured using a locking pin or cotter pin, ensuring the ball and socket joint remain intact during operation.
Made from high-strength steel, often coated for corrosion resistance, these caps are engineered for high-stress environments.
Applications:
Common in high-voltage transmission lines and substations.
Suitable for use in suspension strings where vibration damping is critical.
Advantages:
Provides a secure, stable connection, even under dynamic loading conditions.
Excellent for high-tension installations requiring strong mechanical integrity.
3. Tongue Type Suspension Insulator Caps
Design & Features:
The tongue type cap has a flat, extended plate with a hole that connects to the clevis of another fitting or directly to a conductor clamp.
Typically forged from durable metal materials, ensuring robustness and reliability in various conditions.
Its straightforward design makes it lightweight yet highly functional for specific configurations.
Applications:
Used in configurations requiring direct attachments or where space constraints make other caps impractical.
Common in low to medium-voltage installations and certain specialty high-voltage setups.
Advantages:
Simple design allows for quick and efficient installation.
Lightweight, making it suitable for situations with weight restrictions.
Each type of suspension insulator cap is designed to meet specific needs in power transmission systems. The clevis type excels in flexibility and strength, the socket type in stability and durability, and the tongue type in simplicity and efficiency. Selecting the appropriate cap type ensures system reliability, safety, and optimal performance in different operational contexts.